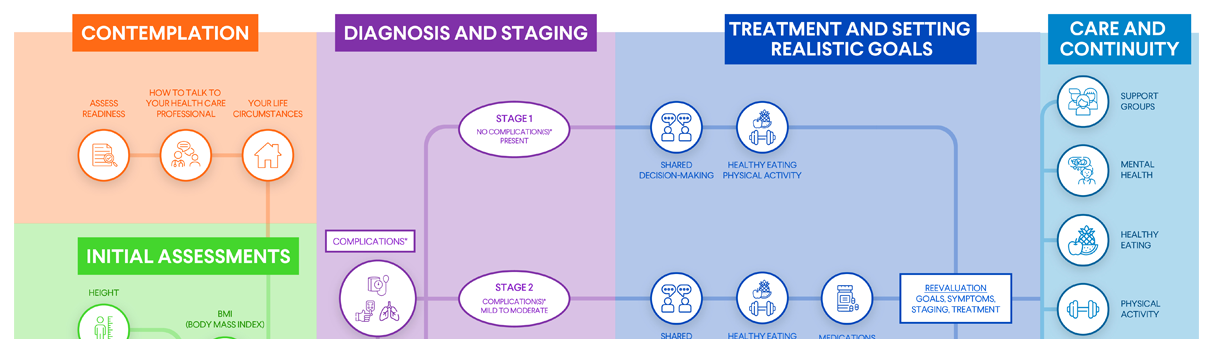
Contemplation
Initial Assessment
Initial Assessment
The initial assessment of obesity is crucial, as it provides a comprehensive understanding of your health status, risk factors, and specific needs related to obesity management. It allows your health care professional to gather important information about your medical history, lifestyle habits, and any underlying medical conditions or complications associated with obesity. With a thorough initial assessment, your health care professionals can develop personalized and effective treatment plans, set realistic goals, and provide appropriate interventions to support you in your journey.
Below is a list of initial assessments you can discuss with your health care professional.
Body Mass Index
All adults should be screened each year using a body mass index (BMI) measurement. This is calculated by dividing weight (in kilograms) by the square of height (in meters).
BMI = kg/m2
Calculate Your BMI
Enter your height and weight below to find your body mass index (BMI)
BODY MASS INDEX
0
Underweight
Healthy Weight
Overweight
Obesity
Below is a BMI chart for adults aged 20 years and older. It applies to most people regardless of sex or body type.
| BMI | Weight Status |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5–24.9 | Healthy Weight |
| 25.0–29.9* | Overweight |
| 30.0 and above** | Obesity |
* 23.0–24.9 for people of South, Southeast, or East Asian descent.
** 25.0 and above for people of South, Southeast, or East Asian descent.
Limitations of BMI
BMI provides a quick, easy, and accurate enough estimate of body fat. However, BMI has its limitations. It accounts for your weight and height but not for factors such as muscle mass, age, or sex. Also, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention note, "BMI does not distinguish between excess fat, muscle, or bone mass, nor does it provide any indication of the distribution of fat among individuals."
The bottom line: While BMI is helpful in screening for overweight and obesity, it's not the final word.
Waist Circumference

Another way to assess for obesity is by measuring the circumference of your abdomen (the area between the chest and pelvis). This can help reveal your risk for complications due to excess body fat, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Waist Circumference Thresholds for Abdominal Obesity in the United States
| Men | Women |
| ≥ 102 centimeters | ≥ 88 centimeters |
| ≥ 40 inches | ≥ 35 inches |
Please note: Waist circumference thresholds can vary depending on region and reference source. Instructions on measuring waist circumference according to the NHANES III protocol can be found here.
History and Physical Examination
Your health care professional will first conduct a thorough physical examination. This will include measuring your height and weight and taking your blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs. They will also ask about your health history, including:
- Any symptoms you're experiencing
- Other health conditions that may be related directly or indirectly to obesity
- Weight-related history, including any challenges related to weight management, exercise, or eating
Behavioral Health
In assessing for obesity, your health care professional may also:
- Screen for depression or anxiety.
- Screen for eating disorders.
Behavioral interventions, such as behavioral therapy, can help you lose weight and improve your overall health. Learn about your options here.
Lab Work (Blood Tests)
Your health care professional may order blood tests to measure your:
- Cholesterol level
- Liver function
- Fasting blood sugar level (to check for diabetes)
After making a diagnosis, your health care professional will discuss your stage of obesity and which treatment options make the most sense for you.
Did You Know?
Lifespan
- Severe obesity (BMI over 40) can shorten lifespan by as much as 14 years.
Prevalence Data
- From 1999 to 2020, the prevalence of obesity in the United States increased from 30.5% to 41.9%.
- The percentage of women who have severe obesity (BMI over 40) is 11.5%, compared with 6.9% of men.
- The prevalence of obesity among children and teens ages 2 to 19 roughly doubled between 1988 and 2018.




 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD